When developing media-rich Android applications, especially using ExoPlayer, you’ll often deal with MediaItems. These represent audio or video items that you want to play. Understanding how to manipulate these items and manage them using Kotlin collections is essential for building dynamic playlists and media queues.

This article covers:
- Creating
MediaItems using the Builder pattern - Adding and removing items from Kotlin lists
- Differences between arrays and lists in Kotlin
- Useful collection operations for working with media items
Creating MediaItem in Kotlin
The MediaItem class in ExoPlayer is built using the Builder pattern. Here’s how to create one:
val mediaItem = MediaItem.Builder()
.setMediaId("media123")
.setUri("https://example.com/media.mp4")
.build()
You can also include optional metadata:
val mediaMetadata = MediaMetadata.Builder()
.setTitle("Sample Video")
.setArtist("Sample Artist")
.build()
val mediaItem = MediaItem.Builder()
.setMediaId("media123")
.setUri("https://example.com/media.mp4")
.setMediaMetadata(mediaMetadata)
.build()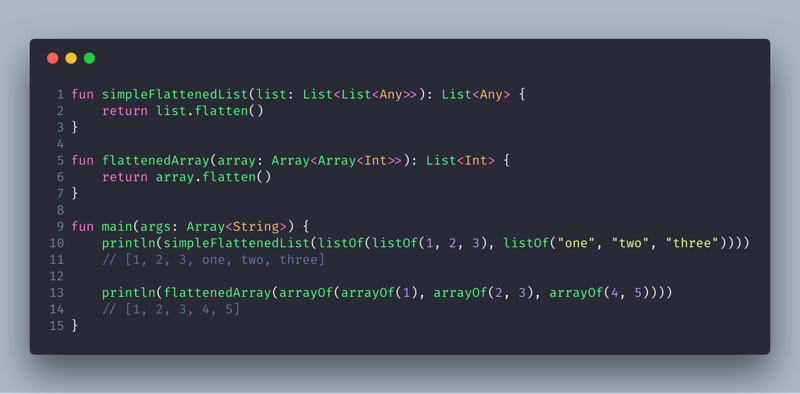
Using Lists to Manage MediaItems
Kotlin offers powerful support for managing collections, such as lists. Here’s how you can manage a playlist:
Creating a Mutable List
val mediaList: MutableList<MediaItem> = mutableListOf()
Adding Items
mediaList.add(mediaItem)
Adding Multiple Items
val secondItem = MediaItem.Builder()
.setMediaId("media456")
.setUri("https://example.com/media2.mp4")
.build()
mediaList.addAll(listOf(mediaItem, secondItem))
Inserting at a Specific Index
mediaList.add(1, mediaItem) // Inserts at position 1
Removing Items
mediaList.remove(mediaItem) // By object
mediaList.removeAt(0) // By index
Iterating Through the List
Kotlin supports various ways to iterate:
for (item in mediaList) {
println(item.mediaMetadata?.title)
}
Or with forEach:
mediaList.forEach {
println(it.mediaMetadata?.title)
}
Arrays vs Lists in Kotlin
| Feature | Array | List |
|---|---|---|
| Mutability | Fixed size, mutable values | List is read-only, MutableList is mutable |
| Declaration | arrayOf(item1, item2) | listOf(item1, item2) or mutableListOf(...) |
| Use Case | Performance-critical fixed-size collections | General-purpose dynamic collections |
Converting Between Array and List
val mediaArray = mediaList.toTypedArray()
val newList = mediaArray.toMutableList()
Advanced Collection Operations
Filtering
val filteredList = mediaList.filter { it.mediaMetadata?.title?.contains("Sample") == true }
Mapping
val titles = mediaList.map { it.mediaMetadata?.title ?: "Untitled" }
Sorting (by title)
val sortedList = mediaList.sortedBy { it.mediaMetadata?.title }
Conclusion
Working with MediaItems and Kotlin collections like List, MutableList, and Array is both flexible and powerful. Whether you’re creating a video playlist, podcast player, or a full-featured music app, understanding these fundamentals will help you build efficient and maintainable code.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a regular List to manage a playlist?
A: You can use List, but it’s immutable. Use MutableList if you plan to add/remove items dynamically.
Q: What is the difference between List and ArrayList in Kotlin?
A: ArrayList is a Java class. MutableList is Kotlin’s recommended abstraction which can be backed by ArrayList or other implementations.
Q: How do I clear all media items from a list?
A: Use mediaList.clear() if it is a MutableList.
Featured Code Snippet: Insert MediaItem Into List
val updatedMediaItems: MutableList<MediaItem> = mutableListOf()
val mediaItem = MediaItem.Builder()
.setMediaId("id1")
.setUri("https://example.com/video.mp4")
.build()
updatedMediaItems.add(mediaItem)